Our News

15July,2021
HOW ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS WORK
A CAR'S ELECTRICAL SYSTEM IS NOT THAT COMPLICATED
Every car's electrical system is composed of a wiring harness that connects various computer, controllers, lights, actuators, motors and switches. This electrical system is intergraded throughout the car to communicate with each part using a central computer which runs the engine or main electric motor. The battery is responsible for supplying power to the car while the engine is not running but in electric cars the battery does all of the work while powering the motor. High amperage circuits are designed with larger components to handle the load without failing. Common maintenance includes inspecting electrical connectors that are visible including the battery cables.
WHAT GOES WRONG?
The most common problems with electrical systems are a short or open circuit. A short circuit is what happens when a wire has rubbed through to ground causing a fuse to blow. An open circuit is what happens when a connection stops working because of a broken wire or a bad conductivity. Low battery voltage can cause strange problems to the electrical components of the car due to insufficient operating voltage. Because of the construction of wiring connectors they can sometimes create high resistance which causes heat making the connector have an open circuit. When performing wiring repairs a wiring schematic is sometimes necessary to trace wires or locate a component.
LET'S GET STARTED
The electrical system of any vehicle performs the same function. To deliver and monitor electrical power to various devices and sensors while under control of the computer system or a passenger inside the car.
Wiring harness are groups of wires which are taped up in plastic tubes and routed around the car and throughout the engine compartment.
A wiring harness has many connectors that can serve as an extension to the main harness which allows routing to devices which are located beyond the reach of the main harness.
Connectors are disconnected by depressing a small tab on the side of the connector. Once apart the male side of the connector is designed with terminals that protrude outward which fit into sockets on the female side. Electrical or wire connectors can vary from a single terminal to many terminal depending on the application. Wire and connectors vary in size due to different amperage loads for each circuit.
A device connector is used to connect to a particular item in the electrical system such as ignition coils which are shown in the image below. A safety is used to securely attach the connector to a device which adds an extra layer of protection from accidental disconnection. This safety clip must be removed before the connector can be released.
An electronic throttle control actuator is responsible for metering air flow into the engine which controls engine speed. A throttle control sensor located near the foot pedal supplies feedback data to the computer which activates the actuator. The throttle control system is integrated into the ABS, cruise control and traction control systems. In older vehicles throttle action was performed by a manually controlled throttle cable which is actuated by the driver's right foot.
The anti-lock brake system controller is an electronic system that helps prevent the wheels from skidding in panic stop and is integrated into the traction control system.
Sensors provide feedback data to the main computer which in turn will illuminate the brake warning light when fluid levels have decreased.
Sensors such as the camshaft angle sensors use thin metal windings which break a magnetic field as the shaft rotates causing a pulse that is sensed by the computer.

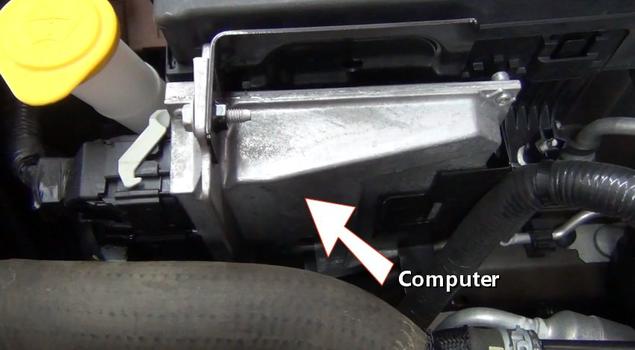
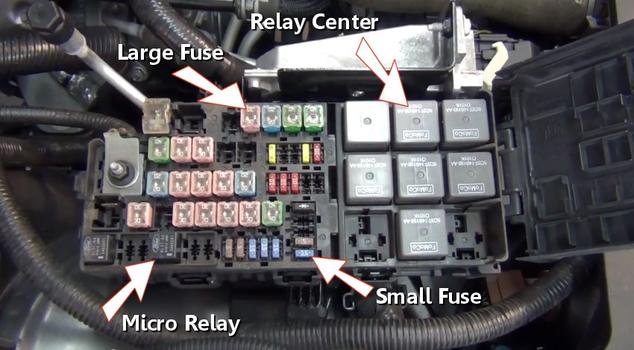
A power distribution center is used to route positive battery power throughout the vehicle using relays and fuses. This center is powered directly off of the positive post of the battery using a positive battery cable.
Inside the PDC are many fuses and relays which protect and control the many electrical circuits such as fuel pump and fuel injection systems. Fuses are used to safeguard electrical circuits and are designed to pop stopping the voltage flow in the event of a power overload or short circuit protecting the circuit wire from burning.
A set of control relays act as the main switching center of the electrical power. These relay's act as electronic switches that are controlled by the computer or by a manual switch. Once engaged the relay connects a circuit which activates a particular device.
A set of large amperage fuses protect high amperage circuits such as the cooling fan, starter solenoid and headlights. A observation window is provided to inspect the fuse's condition.
Medium duty fuses are used to protect average amperage circuits such as power windows and seat heaters. These fuses also provide an observation window which is needed for inspection.
Finally low amperage fuses are used to protect smaller amperage circuits such as tail lights and interior lighting. These fuses are easily checked using a test light.
The battery supplies both positive and ground circuits which complete the electron cycle. The positive side of the system circuit starts at the PDC provided by the battery.
The automotive battery is designed as an electrical storage device and is responsible for delivering electrical power when the engine is not in operation. All batteries possess a negative (ground) and positive (power) attribute of an electrical power system. These connections should be free of corrosion and rust as contaminates hinder the proper operation of electrical circuits. A periodic inspection and test of the battery is necessary to avoid roadside failures. Battery terminals can develop corrosion due to the flow of ions. Terminal and cable cleaning is necessary to remedy this condition.
CATEGORY
LATEST POST


HOW TO FIX BLACK SMOKE FROM EXHAUST
HOW TO CHECK TIRE AIR PRESSURE

HOW TO REPLACE A REAR AXLE BEARINGS AND SEALS 3/4 AND 1 TON

HOW TO FIX POWER STEERING PROBLEMS